
5 New anticoagulants such as oral direct factor Xa inhibitors and direct thrombin inhibitors are becoming available as alternatives to warfarin. For mechanical mitral valve or combined mitral and aortic valves, the target INR is 2.5–3.0. For most warfarin indications, the target international normalised ratio (INR) is 2.0–3.0 (VTE and single MHV excluding mitral). Common indications for the use of warfarin in the community include stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation (AF), preventing thrombus formation in patients with mechanical heart valves (MHV), and treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE). 3, 4 Despite the associated bleeding risk, warfarin remains the most commonly prescribed anticoagulant in Australia and New Zealand. 1, 2 Therefore, strategies to manage over-warfarinisation and warfarin during invasive procedures are important. Patients on long-term therapy have a risk of 1%–3% per year for haemorrhage leading to hospitalisation or death.

W arfarin is effectively used in a wide range of thromboembolic disorders for primary and secondary prevention. Perioperative management of anticoagulant therapy requires an evaluation of the risk of thrombosis if warfarin is temporarily stopped, relative to the risk of bleeding if it is continued or modified. Prothrombinex-VF use for warfarin reversal should be restricted to emergency settings. If necessary, warfarin can be withheld for 5 days before surgery, or intravenous vitamin K 1 can be given the night before surgery. For minor procedures where bleeding risk is low, warfarin may not need to be interrupted. Surgery can be conducted with minimal increased risk of bleeding if INR ≤ 1.5. Vitamin K1 is essential for sustaining the reversal achieved by PCC or FFP.
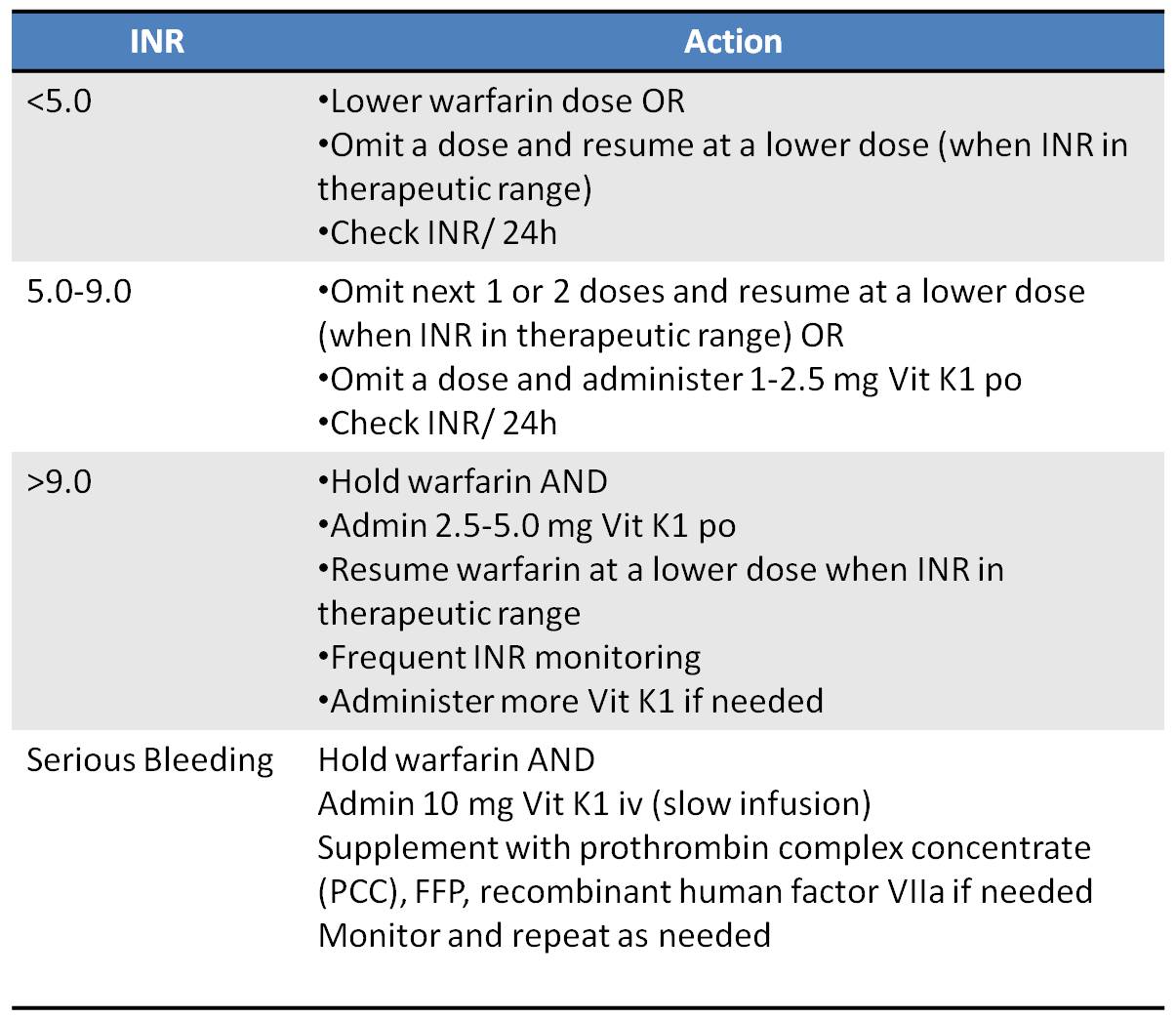
FFP can be used when Prothrombinex-VF is unavailable. FFP is not routinely needed in combination with Prothrombinex-VF. It contains factors II, IX, X and low levels of factor VII. Prothrombinex-VF is the only PCC routinely used for warfarin reversal in Australia and New Zealand. When oral vitamin K 1 is used for this purpose, the injectable formulation, which can be given orally or intravenously, is preferred.įor immediate reversal, prothrombin complex concentrates (PCC) are preferred over fresh frozen plasma (FFP). Vitamin K 1 can be given to reverse the anticoagulant effect of warfarin.

Risk factors for bleeding with warfarin use include increasing age, history of bleeding and specific comorbidities.įor patients with elevated INR (4.5–10.0), no bleeding and no high risk of bleeding, withholding warfarin with careful subsequent monitoring seems safe. For mechanical mitral valve or combined mitral and aortic valves, the target INR is 2.5–3.5. Statistics, epidemiology and research designįor most warfarin indications, the target international normalised ratio (INR) is 2.0–3.0 (venous thromboembolism and single mechanical heart valve excluding mitral).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
